As an additional measure to minimize the potential for off-site movement of dicamba, an approved volatility reduction agent (VRA), or also referred to as pH-buffering agent, is now required by the United States Environmental Protection Agency to be tank mixed with over-the-top dicamba products (i.e., Engenia, Tavium plus VaporGrip, and XtendiMax with VaporGrip). These buffering agents reduce changes in spray solution pH by scavenging available protons in solution thus reducing the formation of dicamba acid (volatile form of dicamba).
While our lab has conducted extensive research with the VRA VaporGrip Xtra (potassium acetate as the active ingredient; several products are now commercially available) over the past two years, we haven’t had the opportunity yet to assess the impact of the new BASF VRA Sentris (potassium carbonate as the active ingredient) on spray solution pH, dicamba volatility, and weed control. Our preliminary work conducted with potassium carbonate (pure form) in 2020 in partnership with Dr. Steve Li, Extension Specialist and Assistant Professor at Auburn University, indicated that this salt can increase spray solution pH and reduce dicamba volatility (Striegel et al. 2020).
Last week, Dr. Tommy Butts, Assistant Professor and Extension Weed Scientist with the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture, shared an issue encountered by applicators regarding pressure and foam build up in the spray tank when Sentris and glyphosate were tank mixed (see: “Sentris and Glyphosate Tank-Mix Compatibility Problems”). The report from Dr. Butts, communication with Dr. Vince Davis, BASF Tech Service Rep for Wisconsin and Northern Illinois, and recent questions from stakeholders about Sentris VRA prompted our lab to run a preliminary solution pH study similar to the work conducted by Striegel et al. 2021 (see: “Spray Solution pH as Influenced by Synthetic Auxin Formulation and Spray Additives”).
Study Methodology
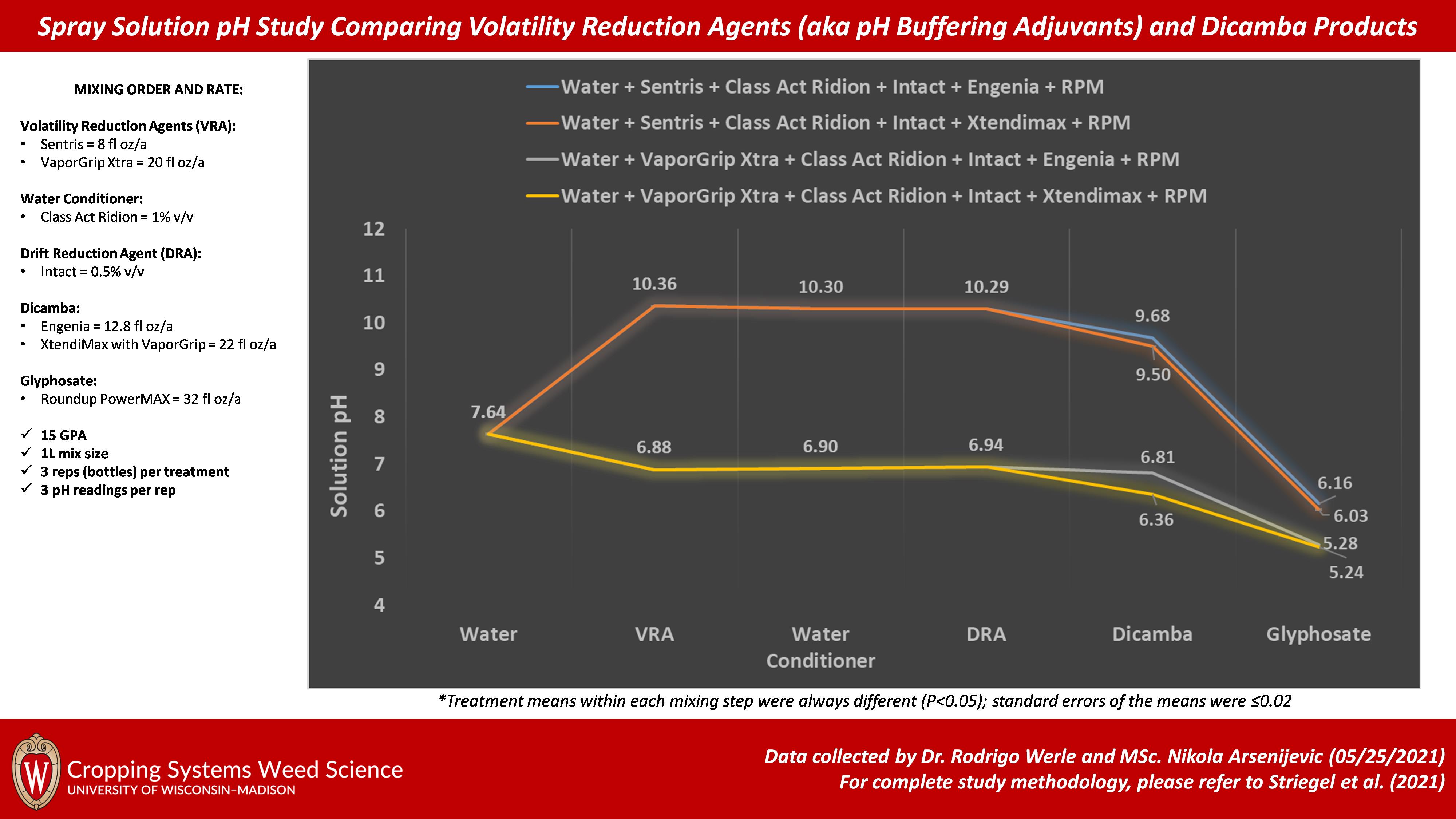
For this study comparing two VRAs (Sentris and VaporGrip Xtra) and two dicamba herbicides (Engenia [dicamba BAPMA salt] and Xtendimax with VaporGrip technology [dicamba DGA salt + VaporGrip), we evaluated the solution pH as products were added to the spray solution following the manufacturers’ tank mix recommendations. Herbicide solution treatments were prepared by mixing tap water from Arlington Agricultural Research Station, WI (initial pH of water source was 7.64±0.02 [average ± standard error]) with additional components to a total volume of 1L (simulating a 15 GPA carrier volume). Solution pH was measured as components were added and thoroughly agitated in solution. Solution pH was measured using an Oakton pHTestr 50 Waterproof Pocket pH Tester, Premium 50 Series probe. For pH readings, ~100 ml of treatment solution was poured into a disposable plastic cup and 3 readings were taken; solution was then immediately returned to the bottle. Each treatment was replicated 3 times (3 separate bottles). Data were subjected to analysis of variance and means were separated when the treatment effect following the addition of each component was less than P = 0.05 using Fisher’s protected least-significant difference.

Study Treatments:
(components within a treatment appear in mixing order)
Water + Sentris (VRA) + Class Act Ridion (water conditioner) + Intact (DRA) + Engenia (dicamba) + Roundup PowerMAX (glyphosate)
Water + Sentris (VRA) + Class Act Ridion (water conditioner) + Intact (DRA) + Xtendimax with VaporGrip (dicamba) + Roundup PowerMAX (glyphosate)
Water + VaporGrip Xtra Agent (VRA) + Class Act Ridion (water conditioner) + Intact (DRA) + Engenia (dicamba) + Roundup PowerMAX (glyphosate)
Water + VaporGrip Xtra Agent (VRA) + Class Act Ridion (water conditioner) + Intact (DRA) + Xtendimax with VaporGrip (dicamba) + Roundup PowerMAX (glyphosate)
Product Rates:
- VRA: Sentris = 8 fl oz/a or VaporGrip Xtra = 20 fl oz/a
- Water conditioner: Class Act Ridion = 1% v/v
- Drift Reduction Agent (DRA): Intact = 0.5% v/v
- Dicamba: Engenia = 12.8 fl oz/a or XtendiMax with VaporGrip = 22 fl oz/a
- Glyphosate: Roundup PowerMAX = 32 fl oz/a
Study Results
Outcomes
- VRA comparison: Sentris had a bigger impact increasing solution pH when compared to VaporGrip Xtra
- Water conditioner: Class Act Ridion didn’t have a major impact on solution pH
- DRA: Intact didn’t have a major impact on solution pH
- Dicamba comparison: Engenia treatments had a slightly higher solution pH when compared to Xtendimax with VaporGrip treatments
- Impact of glyphosate: glyphosate had a bigger impact on reducing solution pH in the Sentris treatments when compared to VaporGrip Xtra; however, the final solution pH was higher for the treatments containing Sentris (6.03-6.16) when compared to VaporGrip Xtra (5.24-5.28)
- Future work: we intend to evaluate the impact of Sentris on dicamba volatility and broad spectrum weed control during the 2021 growing season
Recommendations
- Always follow the product label, including the recommended product mixing order
- To mitigate dicamba off-site movement via vapor drift, the use of a VRA is now mandatory for over-the-top applications of dicamba in dicamba-tolerant soybeans
- When using an inductor tank for mixing, add one product at a time and flush the system between products
- If mixing Sentris VRA with glyphosate, consider adding an approved defoamer to reduce foam production in the tank and assure the spray system is well-ventilated (not enclosed) to reduce potential pressure build up issues. In our study, increased pressure was detected in the bottles when Sentris and glyphosate were mixed and the bottles were kept enclosed with a lid; when bottles were kept without the lid for >5 minutes following the glyphosate addition to the Sentris containing solution, the pressure from the chemical reaction in the tank was allowed to dissipate (data not shown)
Acknowledgements: Many thanks to Nikola Arsenijevic, UW-Madison Weed Science Research Assistant, for the assistance with pH measurements and to our WiscWeeds lab for facilitating this study. Drs. Tommy Butts and Vince Davis provided invaluable feedback to this article.
Article written by Dr. Rodrigo Werle, Assistant Professor and Extension Cropping Systems Weed Scientist, Department of Agronomy, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
References:
- Striegel, S., Oliveira, M., Arneson, N., Conley, S., Stoltenberg, D., & Werle, R. (2021). Spray solution pH and soybean injury as influenced by synthetic auxin formulation and spray additives. Weed Technology, 35(1), 113-127. doi:10.1017/wet.2020.89
- Striegel, S., R.D. Langemeier, B.C. Vieira, S. Li, G.R. Kruger, R. Werle. 2020. Evaluation of dicamba vapor reducing agents across different environments. Proceedings of the 75th North Central Weed Science Society of America Annual Meetings, Virtual Conference.
